“Indeed, these Indian Lakes are goodly things, and may be reckon’d amongst the most remarkable structures in the world.” – Pietro della Valle (seventeenth-century Italian traveler to India)
Early-modern European travelers to India were unanimously impressed by the civil engineering works that they saw there, particularly artificial lakes and irrigation systems. I am impressed by these works as well. In the current post, I will explain the historical background of some of the artificial lakes and tanks that I have come across in my explorations of western India.
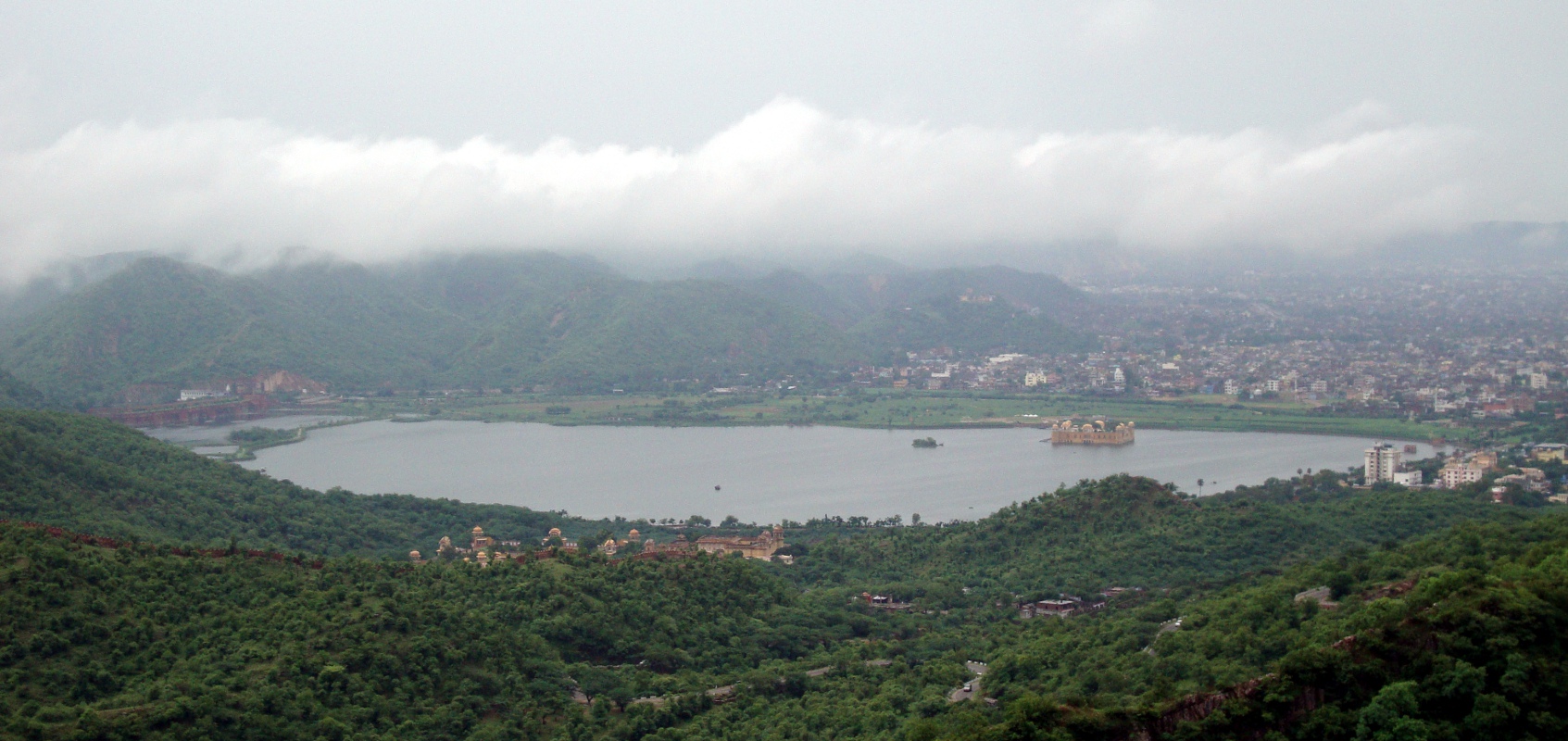
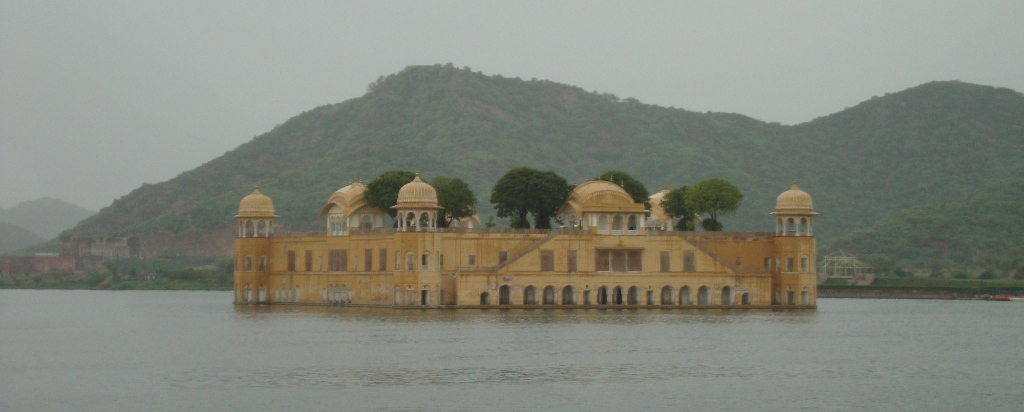
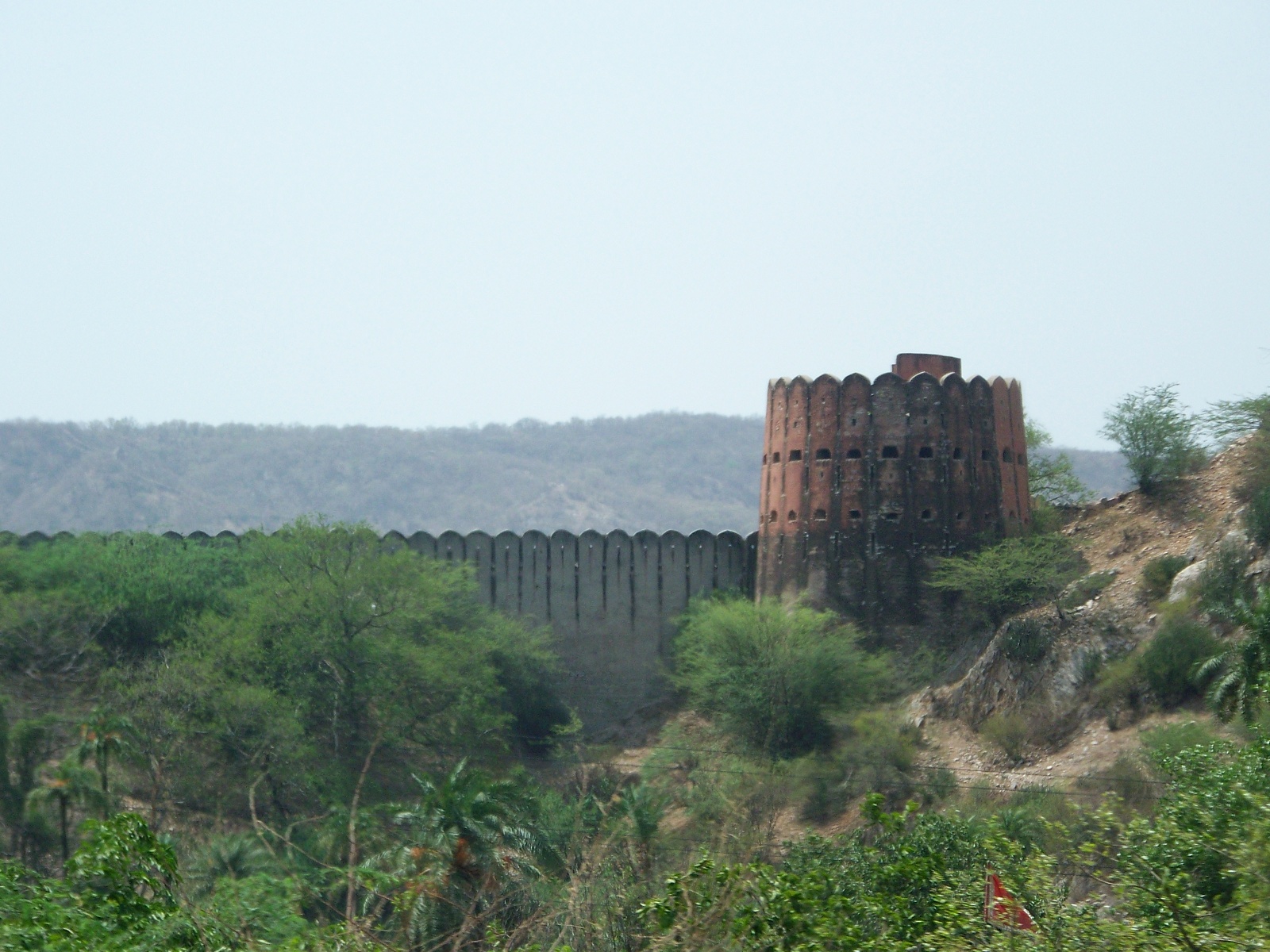
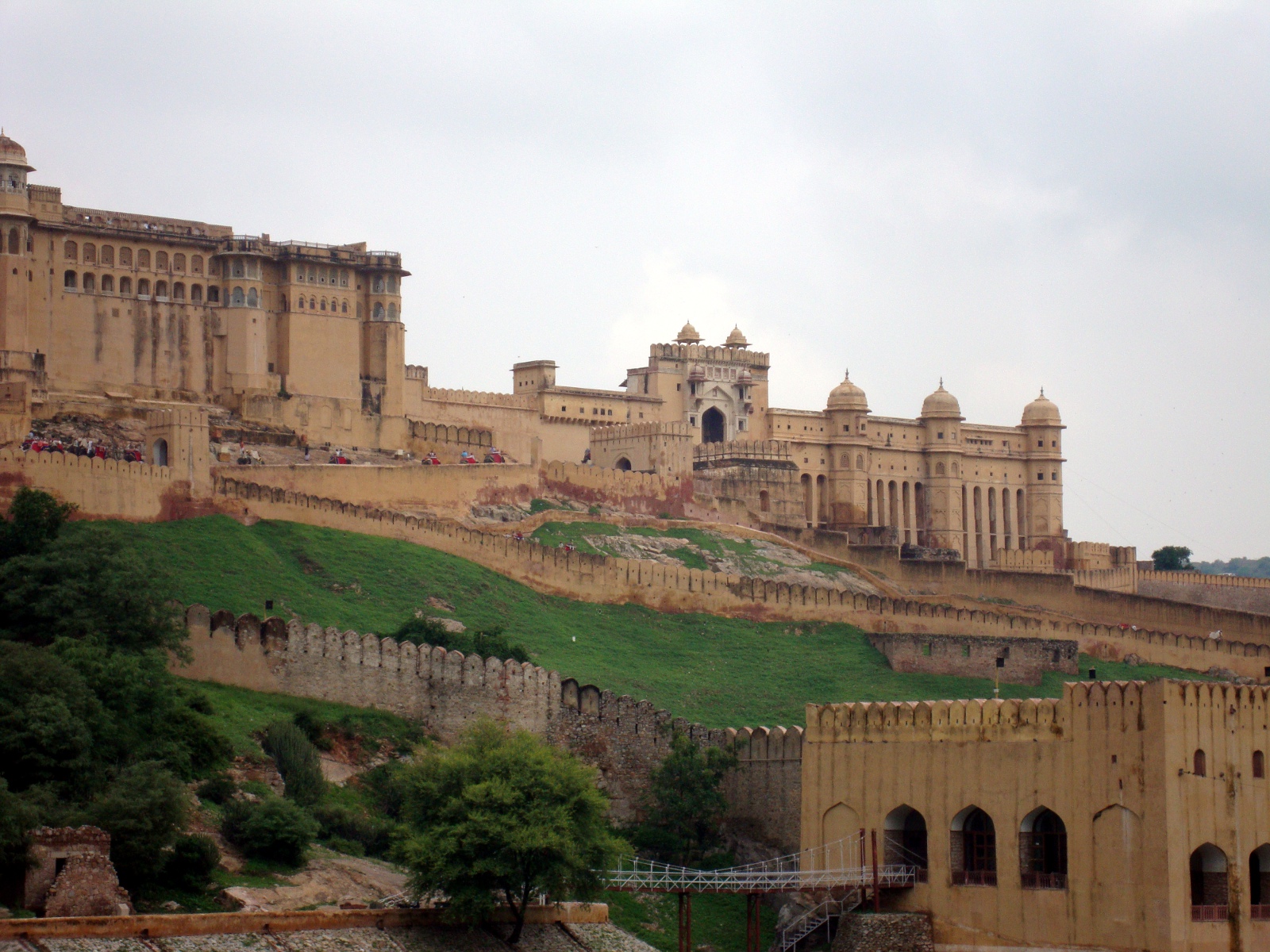
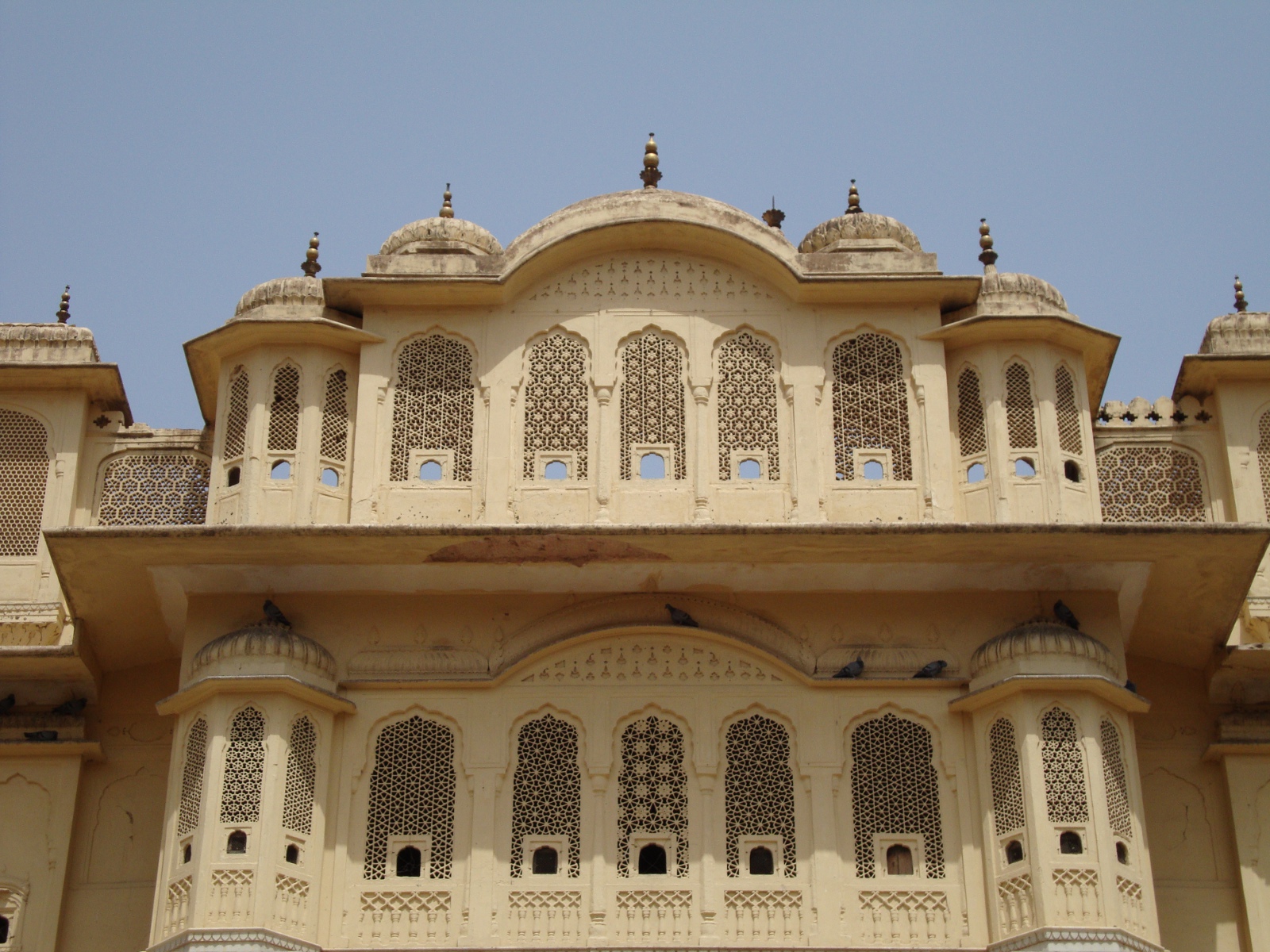
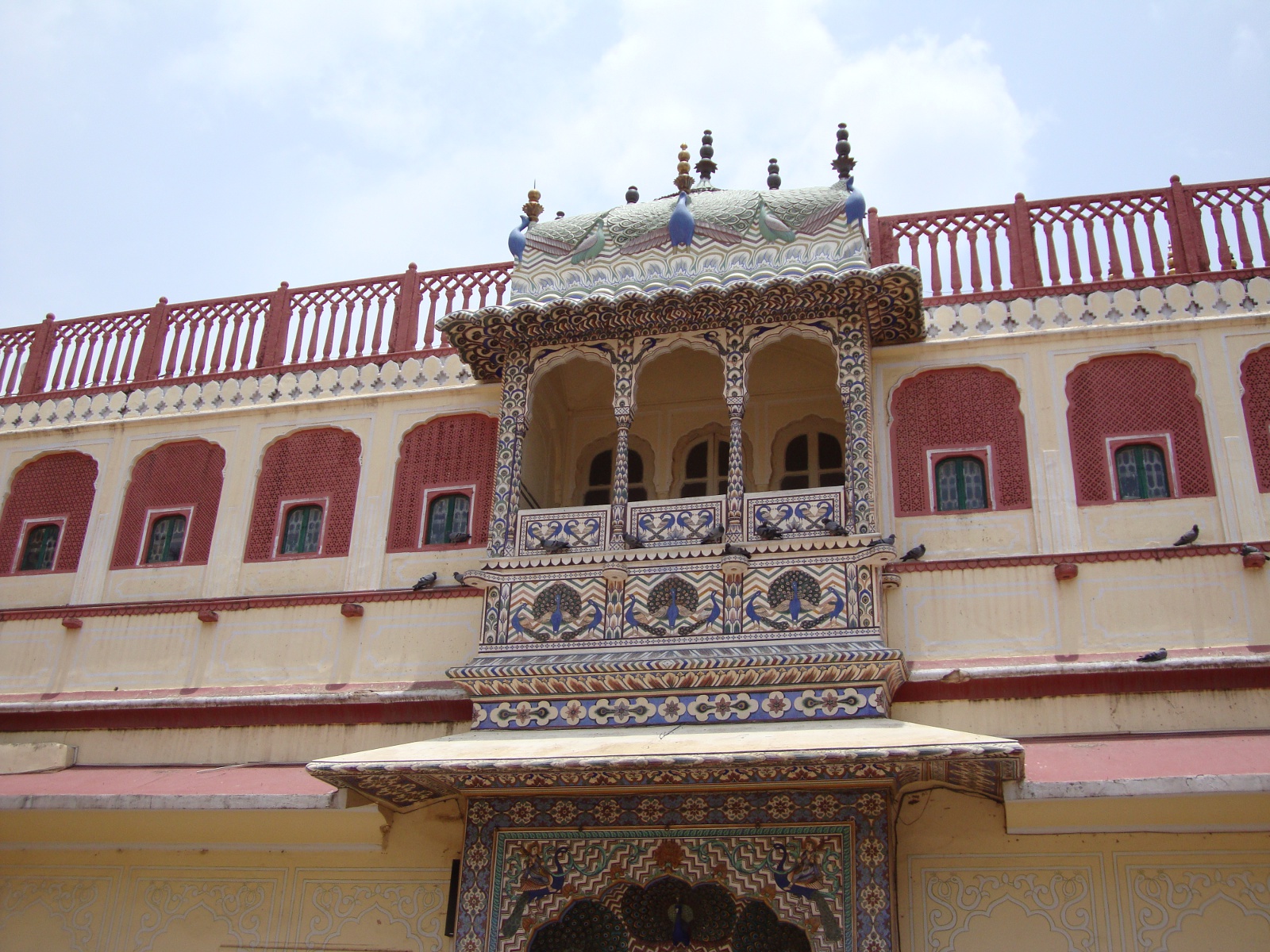
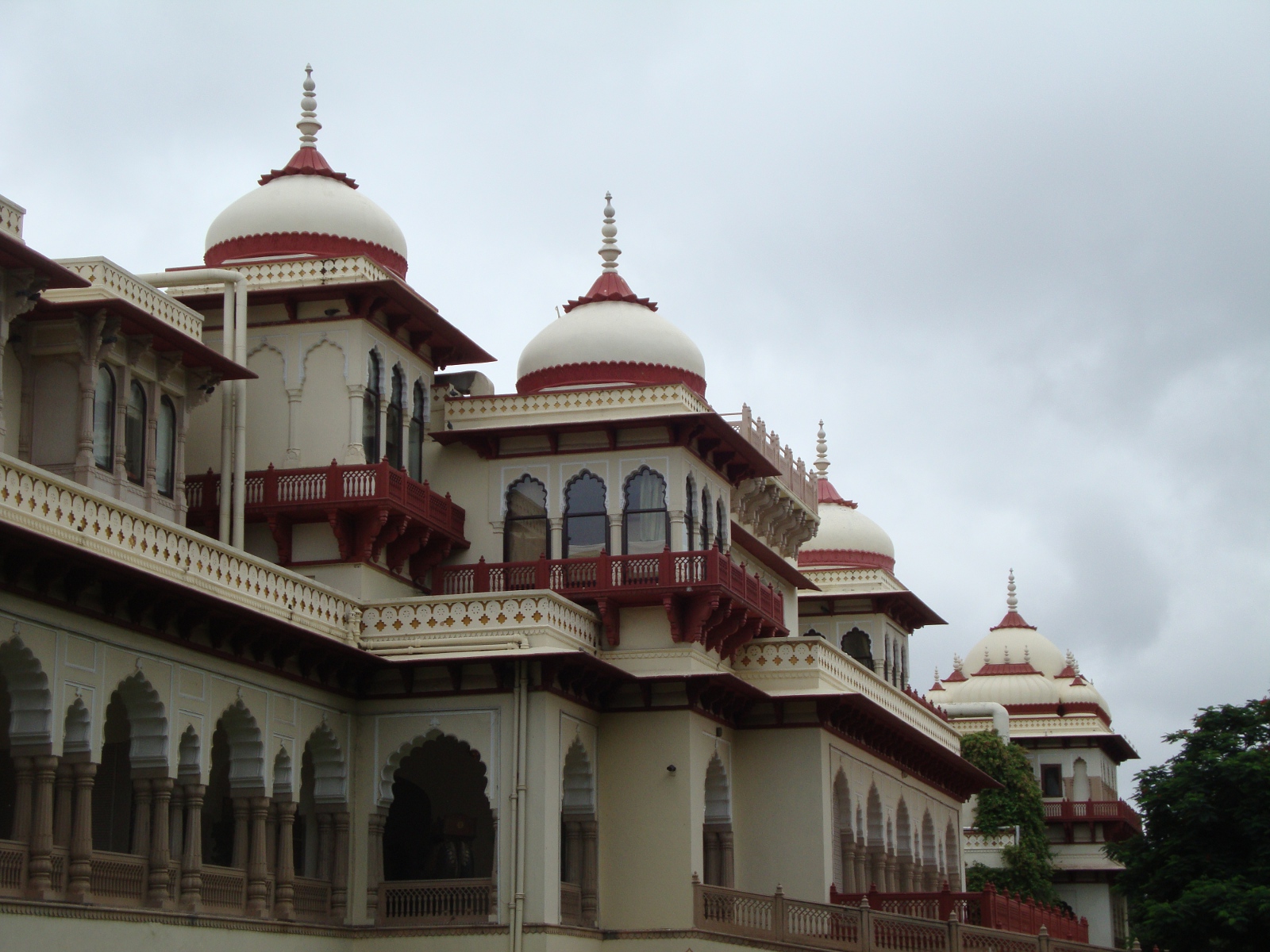
Jal Mahal Sagar is a roughly circular lake just north of the city of Jaipur. The lake takes its name from Jal Mahal (“Water Palace”), a picturesque structure that rises out of the lake near the southwestern shore. Even the dam that impounds the lake is picturesque; it is crenelated like the wall of a Rajput fortress. (See “Batman Goes to India” for a description of Rajput architecture.) The lake had a practical purpose beyond providing a location for the water palace: storing water in order to sure that the city of Jaipur received a reliable supply. Jal Mahal Sagar was an integral part of the original plan of Jaipur when the city was constructed in the 1720s.1
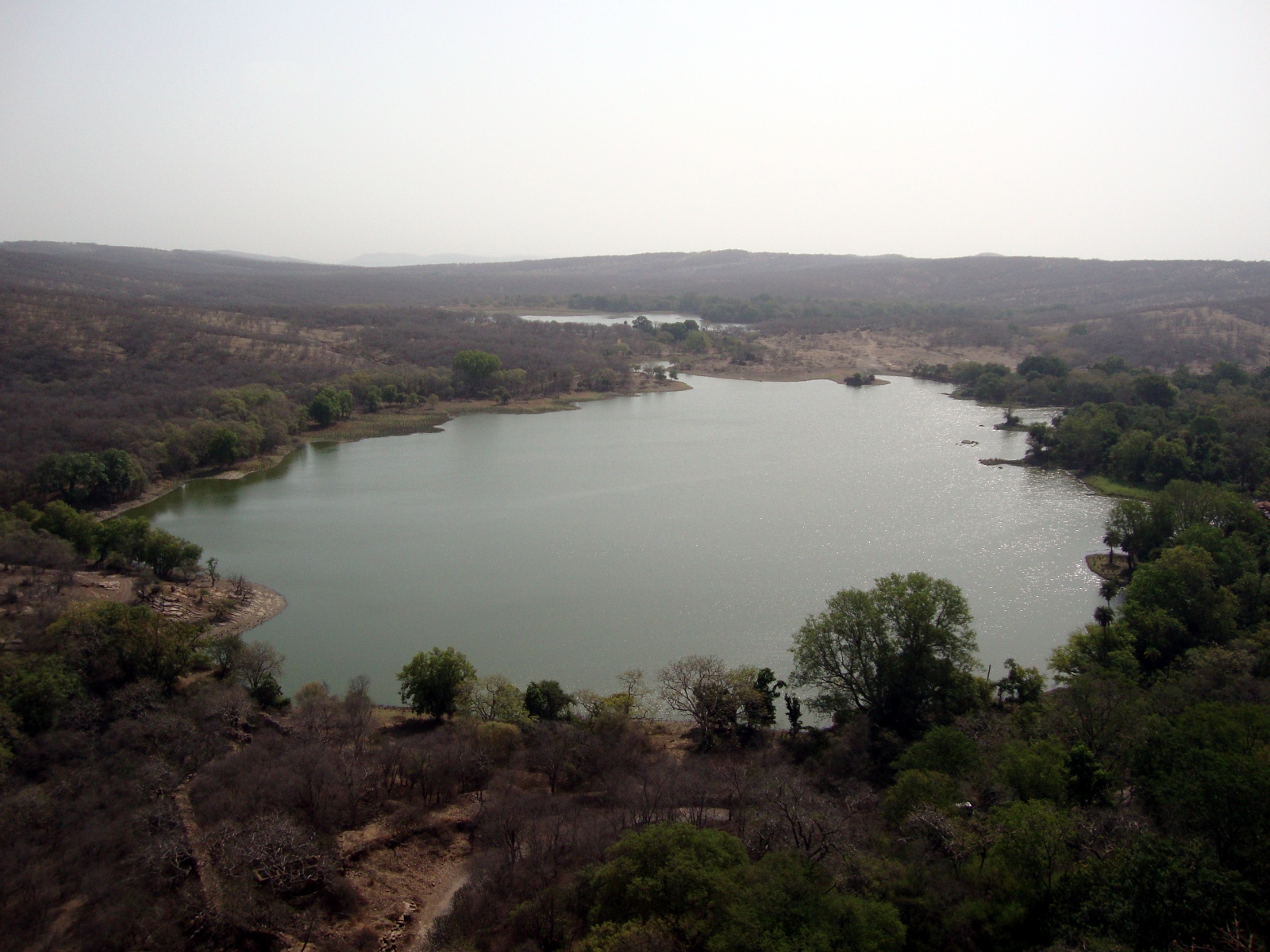
Some artificial lakes have since found uses that their builders did not intend. Take for example the Padam Talao, which now falls within the protected area of Ranthambhore National Park, a tiger reserve in eastern Rajasthan. The park’s crocodiles and deer drink from and wallow in the lake. Humans are not allowed in the water.
Smaller than artificial lakes are tanks. Whereas lakes fill a pre-existing valley behind a dam, tanks are intentionally dug into the ground. Since they do not have to follow the local topography, tanks can be made in whatever shape the builder pleases. Many of them are built with rectangular plans, which I think reflects the Hindu conception of an ordered world and cosmos (as also reflected by the rectangular street plan of Jaipur). It is not the result of European influence.
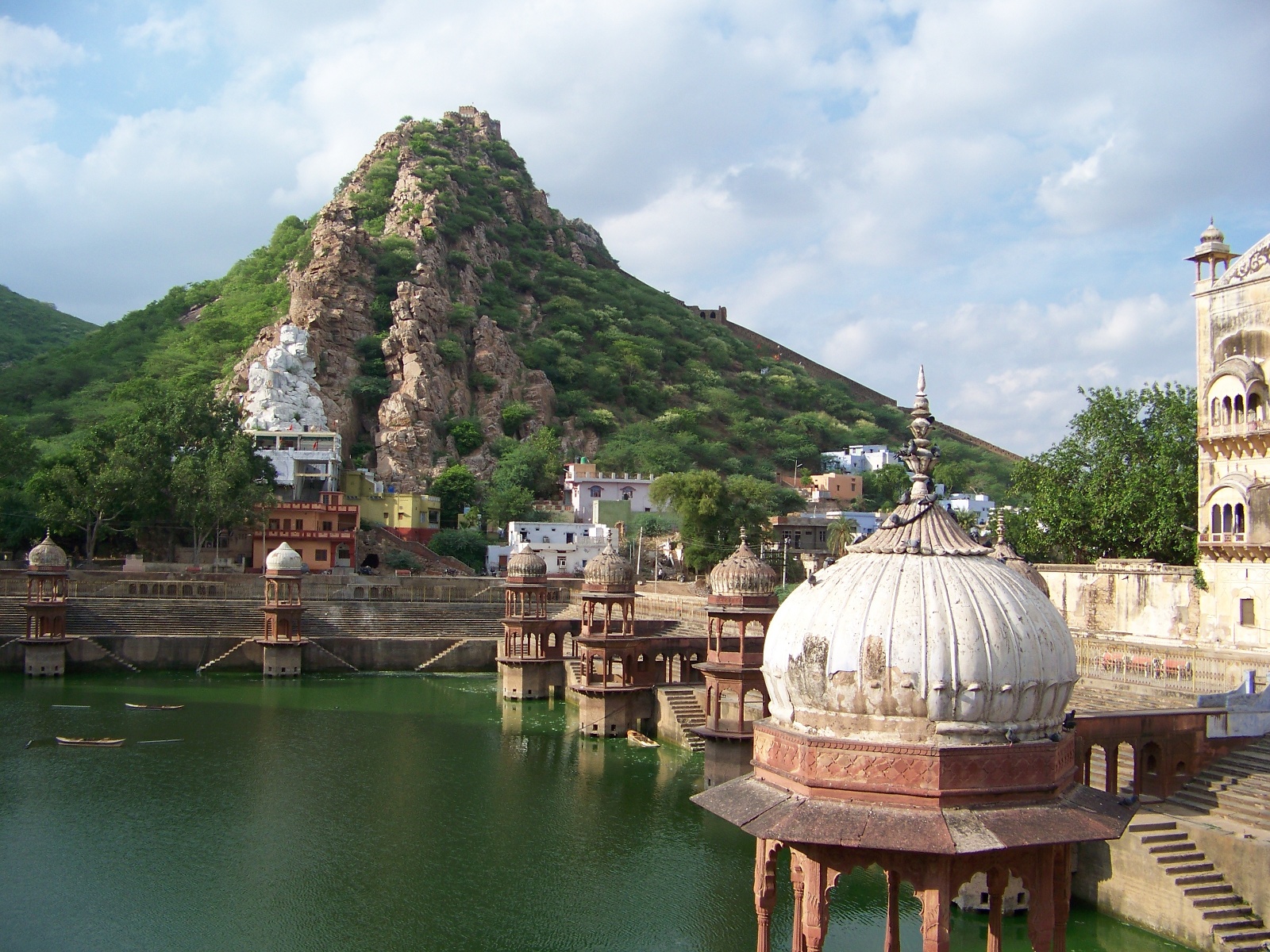
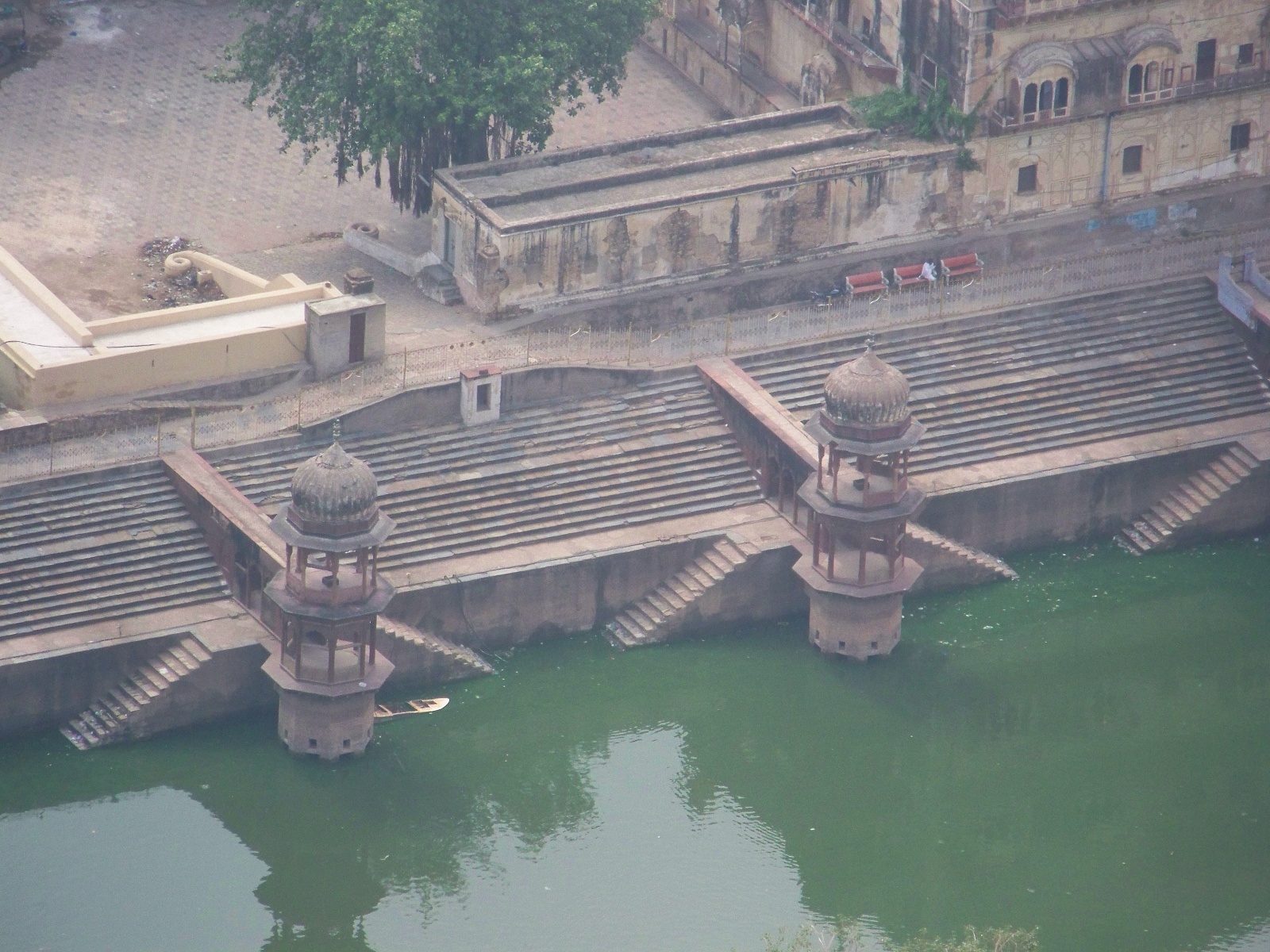
An exemplary tank is the Sagar, located behind the city palace in Alwar. According to the descriptive plaque at the site, the tank was originally dug in the eighth or ninth century, then rebuilt in its present form in 1813 by Maharaja Bakhtawar Singh Ji. The tank is a perfect rectangle, surrounded by steps descending to the water on all sides. Twelve domed pavilions rise from the edge of the water. Today, the water is overgrown with algae, but people still come to the tank to feed the fish that manage to live in the water.
- Giles Tillotson, Jaipur Nama: Tales from the Pink City (New Delhi: Penguin Books, 2006), 20. [↩]